 Sadako was two years old when the atomic bomb was dropped on Hiroshima. She was two kilometers away from where the bomb exploded. Most of Sadako's neighbors died, but Sadako wasn't injured at all, at least not in any way people could see.
Sadako was two years old when the atomic bomb was dropped on Hiroshima. She was two kilometers away from where the bomb exploded. Most of Sadako's neighbors died, but Sadako wasn't injured at all, at least not in any way people could see.
Up until the time Sadako was in the seventh grade (1955) she was a normal, happy girl. However, one day after an important relay race that she helped her team win, she felt extremely tired and dizzy. After a while the dizziness went away leaving Sadako to think that it was only the exertion from running the race that made her tired and dizzy. But her tranquillity did not last. Soon after her first encounter with extreme fatigue and dizziness, she experienced more incidents of the same.
Sadako was a bright, happy girl. She had lots of energy and her parents always had to tell her to sit still. Sadako Sasaki loved to run. She was very excited about being a part of the relay team at her school. This is why she did not tell anyone that she was suffering from dizzy spells when she was running. One time, however, she collapsed in front of teachers and her parents were called. She was hospitalized on February 21, 1955, where her family learned that she had leukemia as a result of the atomic bomb. It was predicted that she would live for no longer than one year.
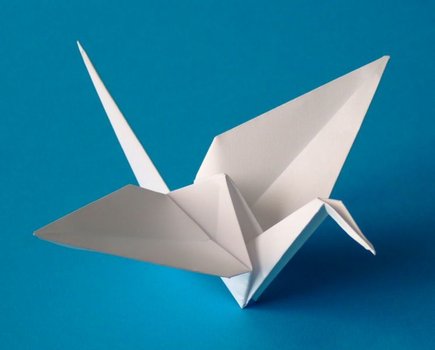 Shortly thereafter, Sadako's best friend, Chizuko, came to visit her. Chizuko brought some origami (folding paper). She told Sadako of a legend. She explained that the crane, a sacred bird in Japan, lives for a hundred years, and if a sick person folds 1,000 paper cranes, then that person would soon get well. After hearing the legend, Sadako decided to fold 1,000 cranes in the hope that she would get well again.
Shortly thereafter, Sadako's best friend, Chizuko, came to visit her. Chizuko brought some origami (folding paper). She told Sadako of a legend. She explained that the crane, a sacred bird in Japan, lives for a hundred years, and if a sick person folds 1,000 paper cranes, then that person would soon get well. After hearing the legend, Sadako decided to fold 1,000 cranes in the hope that she would get well again.
Sadako's family worried about her a lot. They often came to visit her in hospital to talk to her and to help her fold cranes. After she folded 500 cranes she felt better and the doctors said she could go home for a short time, but by the end of the first week back home the dizziness and fatigue returned and she had to go back to the hospital.
Sadako kept folding cranes even though she was in great pain. Even during these times of great pain she tried to be cheerful and hopeful. Not long afterwards, with her family standing by her bed, Sadako went to sleep peacefully, never to wake up again. She had folded a total of 644 paper cranes.
Every one was very sad. Thirty-nine of Sadako's classmates felt saddened by the loss of their close friend and decided to form a paper crane club to honor her. Word spread quickly. Students from 3,100 schools and from 9 foreign countries gave money to the cause. On May 5, 1958, almost 3 years after Sadako died, enough money was collected to build a monument in her honor. It is now known as the Children's Peace Monument, and is located in the center of Hiroshima Peace Park, close to the spot where the atomic bomb was dropped.
Many of the children who helped make the Children's monument a reality participated in the ceremony. Three students, including Sadako's younger brother Eiji Sasaki pulled the red and white tape off the statue to symbolize its completion, while Beethoven's Seventh Symphony was played. The little bell, contributed by Dr. Yukawa, inscribed with "A Thousand Paper Cranes" on the front and "Peace on Earth and in Heaven" on the back, rang out and the sound carried as far as the A-bomb Dome and the Memorial Cenotaph. Adults who supported the group later formed the "Paper Crane Club" in June. (The original Paper Crane Club disbanded in 1997).
Children from all over the world still send folded paper cranes to be placed beneath Sadako’s statue. In so doing, they make the same wish which is engraved on the base of the statue:
"This is our cry, This is our prayer, Peace in the world".
Sadako Sasaki....January 7, 1943 – October 25, 1955 (12 years)
Japanese girl who was two years old when the atomic bomb was dropped on August 6, 1945, near her home by Misasa Bridge in Hiroshima, Japan. Sadako is remembered through the story of attempting to fold a thousand origami cranes before her death, a wish which was memorialized in popular culture.
Memorial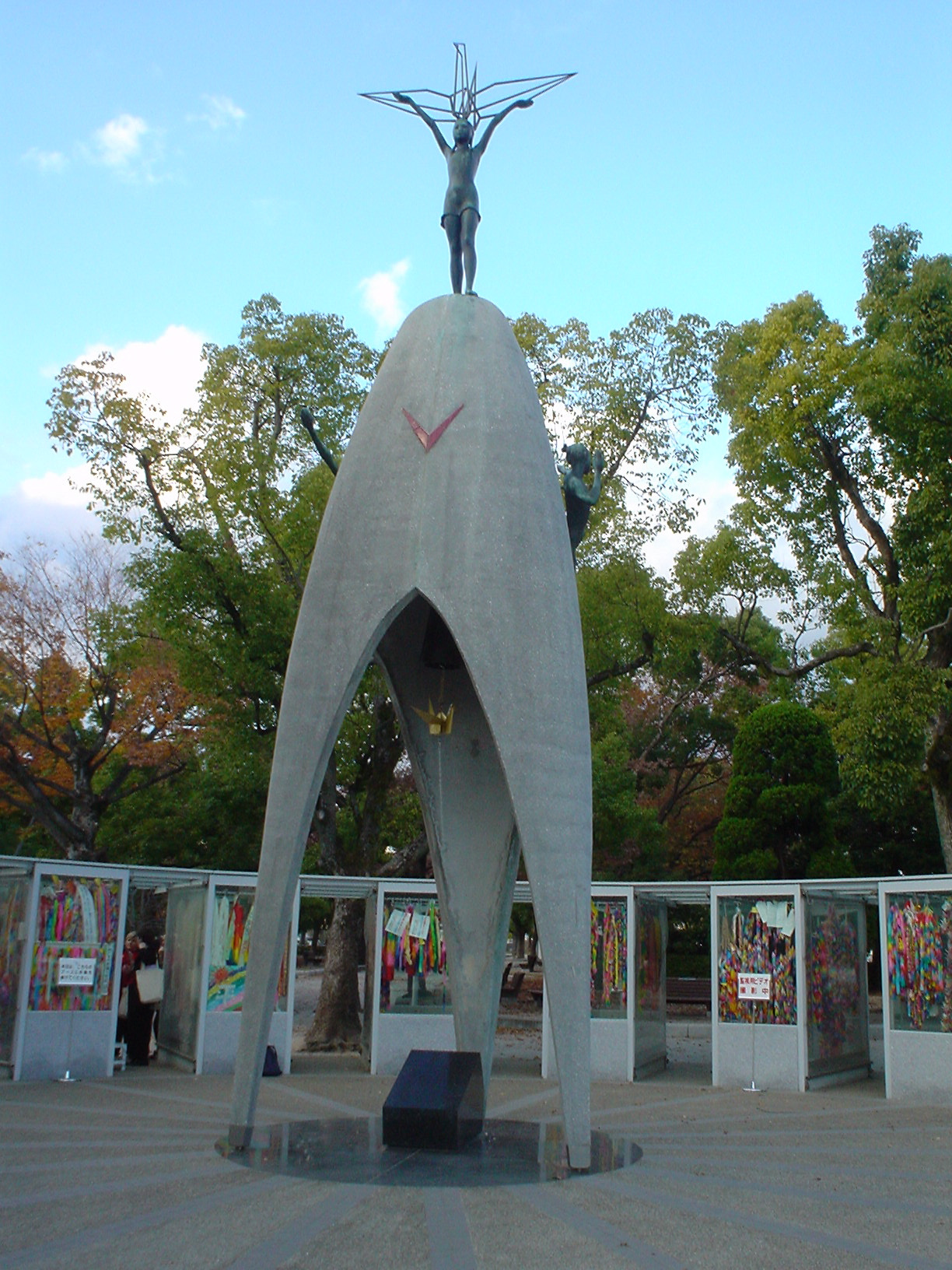

After her death, Sadako's friends and schoolmates published a collection of letters in order to raise funds to build a memorial to her and all of the children who had died from the effects of the atomic bomb. In 1958, a statue of Sadako holding a golden crane was unveiled in the Hiroshima Peace Memorial, also called the Genbaku Dome. At the foot of the statue is a plaque that reads:
"This is our cry. This is our prayer. Peace on Earth."
There is also a statue of her in the Seattle Peace Park. Sadako has become a leading symbol of the impact of nuclear war. Sadako is also a heroine for many girls in Japan. Her story is told in some Japanese schools on the anniversary of the Hiroshima bombing. Dedicated to her, people all over Japan celebrate August 6 as the annual peace day.
In popular culture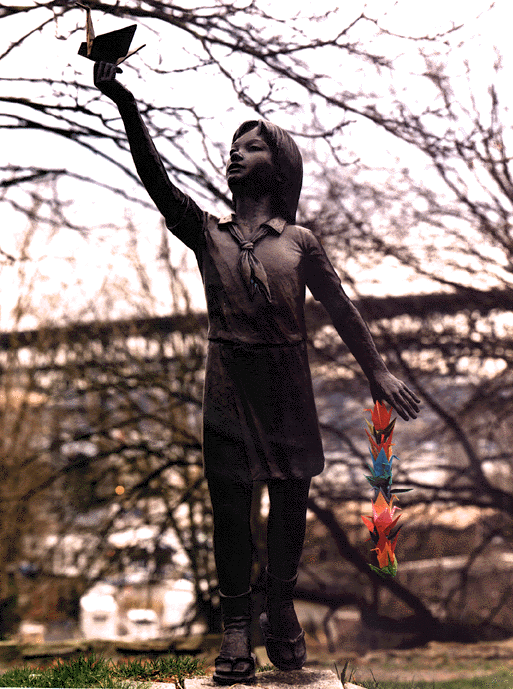 Sadako's story has become familiar to many schoolchildren around the world through the novels The Day of the Bomb (1961, in German, Sadako will leben) by the Austrian writer Karl Bruckner and Sadako and the Thousand Paper Cranes by Eleanor Coerr, first published in 1977.[2] Sadako is also briefly mentioned in Children of the Ashes, Robert Jungk's historical account of the lives of Hiroshima victims and survivors. Her story continues to inspire millions to hope for lasting peace in the world.
Sadako's story has become familiar to many schoolchildren around the world through the novels The Day of the Bomb (1961, in German, Sadako will leben) by the Austrian writer Karl Bruckner and Sadako and the Thousand Paper Cranes by Eleanor Coerr, first published in 1977.[2] Sadako is also briefly mentioned in Children of the Ashes, Robert Jungk's historical account of the lives of Hiroshima victims and survivors. Her story continues to inspire millions to hope for lasting peace in the world.